Lupo Lupus
Member-
Posts
48 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by Lupo Lupus
-
Do you have a framework for what return you require (hurdle rate) to invest in a special situation? Suppose you require 10% on ordinary stocks, what return do you want on a specific special situation? My thinking is that I vary this with the market dependence of the investment. For example, a liquidation where most of assets are already in cash will show little correlation with the market. I may hence compare it to the risk free return (eg government bonds). Contrast this with a liquidation where the company still has to sell a lot of real estate. The payout may then be really low if the market goes south in the meantime and liquidation happens at fire-sale prices. I may hence require the hurdle on stocks, or even higher (think of NYRT -- a leveraged real estate liquidation susceptible to fire-sales). But how to apply this to other situations, like merger arbitrage? In principle the pay-off there might be unrelated to the market -- but maybe not fully as the merger might be called off if the market tanks. Any thoughts on this? Any ressources to read up on this?
-
Buffett alternative to Black Scholes model
Lupo Lupus replied to nickenumbers's topic in General Discussion
I thought this was a very nice point, going much beyond option pricing. Value investors view price drops as changes in market perceptions without (commensurate) changes in true values. Efficient markets however suggest that prices drop because fundamentals have changed. The truth of course lies somewhere in between. Yes prices drop when fundamentals change, but sometimes they do not correctly reflect changes in fundamentals, which opens the door for value investing strategies. -
We all know AlphaVulture, Oddball and the likes ... but what about good news blogs that are relatively unkown? I have not see much in recent years ... except perhaps the outstanding LT3000 blog ...
-
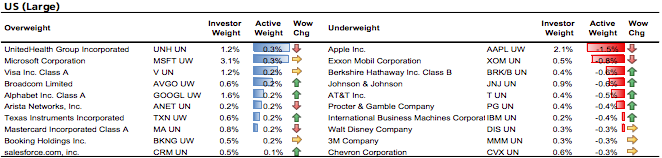
Active share underweighing is enormous though. 0.6 percentage points on a net share of 0.4%. Do you know whether this was equally large in the past?
-
-
Yes, that would be true if the only ETFs were broad-market ETFs like S&P500 tracking funds. But, how much capital also flows into boutique ETFs that specialize in tech? SJ But if this is the argument, then its not about passive investing. If people invest in tech ETF instead of the broad market, its an active decision.
-
Its a great letter but they keep on making the same mistake: they argue that passive investing into ETFs makes the companies with the larger weights get even larger weights => No, ETFs flows means stocks are being bought in proportion to their current weights, so they rather cement existing weights instead of pushing the larger ones even higher .... otherwise great letter with a good overview of many problems facing markets today!
-
What are you using to measure performance, and why? I am talking here from the perspective of a private investor (considerations for portfolio managers who face passive inflows are obviously different). Basically, I am seeing a trade-off. On one hand, money-weighted returns will also capture your asset allocation skills. Eg, converting spare cash to equity when prices are low and expected returns are high. But on the other hand, inflows in most people's portfolios are to some extent passive. For example everybody who mechanically adds new savings to the equity portfolio has effectively passive inflows. Using money-weighted returns will then add noise to the measurement of skills. I am currently using money-weighted returns, as they are easier to calculate for me (given the way I record my trades).
-
It is a very interesting concept. Harley Bassman of PIMCO pointed this out at the end of 2016 as well. The fact that the trade is still alive and well suggests it wasn't a top performer in 2017, but the logic of his trade was sound. The "underpricing" of future dividends was even more pronounced a year ago, so the trade may have well worked. Personally, I am thinking about less in terms of short-term trade but more with the intention to hold to maturity (of course market fluctuations provide an option for exiting earlier).
-
FT Alphaville has an interesting article on dividend derivatives: https://ftalphaville.ft.com/2018/01/10/2197424/why-do-futures-markets-imply-a-depression-level-collapse-in-european-dividends/ Basically long term dividend futures price in a 20% decline in Eurostoxx dividends, something that is unlikely to happen. FTAV argues that there might be an arbitrage opportunity (go long in the long futures). A reason for the potential mispricing is hedging demand by banks. The article also mentions some caveats, and some further are in the comments section. On top of this I can see three more reasons for the low pricing: Payout ratios may decline in the future Firms with less dividends may enter the index The discount to expected value represents a required return (risk premium), similar to stocks. Dividend derivatives are in principle very interesting because you get a claim on something that is not depending on the market (if held until maturity your pay-off is not subject to market vaguaries) and hence provides a good diversification opportunity. Here is also a short overview article on dividend derivatives: https://www.mckinleycapital.com/investing-dividend-strips-using-dividend-derivatives/ Would be interested in your views!
-
Do you use any rule-of-thumb for what you consider a fair level of board compensation, like x % of sales? And if so, what do you use as yardstick (sales, earnings, employees, mcap ...). I have so far not found a quick-and-dirty way to assess the level of board compensation. Also, do you do any adjustments for smaller companies (board compensation is partly a fixed cost and hence will weigh more on smaller firms). EDIT: I realized my post may be ambiguous. I am talking about the *level* of compensation (ie whether its excessive in dollar terms) not *how* management is incentivized (eg fixed vs variable compensation) So when talking about compensation as a % of sales this is just a way to normalize with firm size.
-
Your value investing style through the cycle
Lupo Lupus replied to Lupo Lupus's topic in General Discussion
I like this view. In this way the proportion of different value styles in the portfolio (say optically cheap vs quality) will vary over the cycle, but passively. You buy whatever "style" is cheap so to make full use of current opportunities, without actively adjusting the investing styles or search strategy. I think Cliff Asness has made a similar point as regards to factor investing. -
Is it a good idea to adjust your value investment style depending on the stage of the market cycle? I am not talking about how value investing in general performs over the cycle (which has been analyzed before) but what to choose *within* the value universe. For instance, one view would be that in a depression (2009) to focus on securities that are classic deep value (eg, statistically cheap) and to move into more quality assets later in the cycle (eg, now). Problem with this is that everybody wants to move into quality at this stage, so this may be a self-defeating strategy... Any thoughts on this?
-
I am a big fan of the quarterly letters of GMO. At their website they have them available back to 2007. Does anybody know how to get letters from before that date?
-
Thanks
-
Can google sheets also do currency conversion at historical rates? I have now (bought) an excel add on for this, but would be happy to see a free possibility.
-
I still always keep my eye out for the double loop de loop as a strong signal to stop looking at stocks, turn off my computer, and go to bed. And does the signal work?
-
On the risk of becoming a pariah in the forum: can somebody recommend a good book on technical analysis? (lets say I need it for a good "friend" and not for myself!) Preferrably one that does not just lay-out the strategies but also explains the rationales behind them (eg behavioural foundations or even value foundations). Any suggestions are appreciated!
-
Fiskars Oyj FKRAF was founded 1649 -- seems to be the winner so far. Probably going into my portfolio -- to make it look more respectable!
-
Does anybody know what the oldest, still operating, LISTED company is (worldwide)? Its fairly easy to find lists of the the oldest existing companies, but I could not find any info on the listed ones.
-
I am curious as well -- I also note quite a few of Japanese stocks on my watchlist doing reverse splits.
-
What concept of margin of safey is the best?
Lupo Lupus replied to Lupo Lupus's topic in General Discussion
Could you elaborate? -
What concept of margin of safey is the best?
Lupo Lupus replied to Lupo Lupus's topic in General Discussion
The idea of #3 is to seek "margin of safety" within your modelling assumptions -- but still looking at the expected value in terms of fundamental risk (as opposed to #2). So in the example I do not know the exact value of the pay-off in the good state, and to be conservative I assume the worst (190). Thus expected value is 190/2=95 so MoS is 5 given that price is 90. -
What concept of margin of safey is the best?
Lupo Lupus replied to Lupo Lupus's topic in General Discussion
Thanks -- appreciate your answer. I think I am in fact using all three aspects of MoS simultaneously, which leads of course to muddle thinking. What I dont like about 2. is that it focuses exclusively on the downside of the individual investment. Suppose I choose between investments with high expected return and (low) risk of a considerable loss, and investments with lower expected return but zero risk of big loss. If through my investment life I tend to carry out investments of the first type repeatedly (and size them of course appropriately), my wealth outcome may effectively be safer because of the higher expected return (safer in terms of for example the likelihood of falling below a certain amount I need to retire). So the downside in my *portfolio* may be more protected than in the second case. -
I find the concept of margin of safety fuzzy, it seems to be used in different ways: 1. Price relative to expected value. Suppose there is a binary outcome bet: with 50% probability we get 200 and with 50% probability zero. Price is 90 so MoS is 10 (expected value minus price). 2. How much buffer do I have such that I do not make a loss? This is more a scenario where I want to have a low price that provides buffer against risk. In the above example, there will never be a MoS then as with 50% everything will be lost. 3. Robustness to valuation assumptions: Here the margin of safety provides a buffer against modelling mistakes. Suppose that the 200 in the above example is in estimated, and lies in fact anywhere between 190 and 210. Assuming the lower end (190) I could then arrive at a MoS of 5 if the price is 90. Each concept underlies a different objective -- which one do you find the most attractive one? Does it matter in the first place (in practice) which one to use?